Diarrhea and weight losswere associated with both colonic carcinoids. By far the most common spontaneous gastrointestinal neoplasms in NHPs are ileocecalcolonic adenocarcinomas in rhesus macaques cause up to 50 of tumors identified in rhesus macaques over 20 years old and colonic adenocarcinomas in cotton-top tamarins.

Pdf Use Of An Incontinent End On Colostomy In A Dog With Annular Rectal Adenocarcinoma Semantic Scholar
Cecal adenocarcinomas are reported with increased frequency in aged baboons.
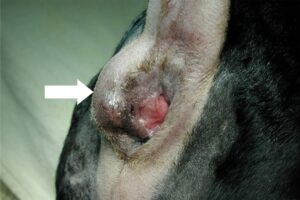
Adenocarcinoma colon dog. Intestinal tumors occur in older dogs median age 10 years. Histopathologic Features of Colorectal Adenoma and Adenocarcinoma Developing Within Inflammatory Polyps in Miniature Dachshunds. When less intensive treatment plans are pursued the prognosis is typically shorter although anal gland adenocarcinoma is one of the most challenging tumor types to predict survival.
Identifying and treating anal sac adenocarcinoma in dogs. Adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphoma are the most common canine intestinal tumors. Colon Cancer in Dogs Explained.
Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumour that originates from the epithelial layer of glandular tissue. Histopathologic diagnoses of the initial biopsy samples were inflammatory. Most of the dogs had clinical signs less than or equal to 12 weeks before examination.
While intestinal cancer is rare in dogs most intestinal tumors are malignant and therefore prognosis is not good. Anal sac adenocarcinoma is reported to represent 2 of all skin tumors and 17 of perianal tumors in dogs12 So although it is an uncommon tumor it is locally invasive. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas can present as chronic epigastric pain nausea vomiting jaundice weight loss anorexia asthenia steatorrhea hepatosplenomegaly thrombophlebitis.
In six of 10 dogs with rectal carcinoma rectal bleeding was seen and rectal prolapse occurred in one. In dogs with colorectal neoplasms the most common clinical signs were straining on defecation and hematochezia. Biopsy samples of colorectal polyps were collected and examined from 67 Miniature Dachshund dogs including 35 cases with an additional biopsy.
The reported incidence of intestinal adenocarcinoma among. Clinical signs in all 78 dogs included tenesmus hematochezia and dyschezia. Adenocarcinomas are malignant tumors found in the glandular structures in the epithelial tissue.
Dogs can develop smaller benign growths polyps or adenomas in the membrane at the end of the colon near the rectum. Dogs with apocrine gland adenocarcinoma treated with surgery and radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy have an average survival of over 25 years. Colorectal neoplasia is an uncommon diagnosis in dogs.
Adenocarcinoma and lymphoma are malignant tumors that make up nearly half of reported cases of colon cancer according to the National Canine Cancer Foundation. The most common gastrointestinal tumors in dogs are adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphosarcoma with adenocarcinoma being the most common. An adenocarcinoma will cause a tumor growth within the apocrine glands in a dog which are located near the rectum.
Lymphoma in a dog will affect the lymphoid tissue in the intestinal tract. Less common tumor types include leiomyoma other sarcomas GISTs carcinoids plasma cell tumors and mast cell tumors. Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach Intestine or Rectum in Dogs.
27 Of 170 dogs with colorectal neoplasia documented in 6 retrospective studies 38 100. They are usually very aggressive and form often metastases. Monest sites in man and the dog are the colon and duodenum 8.
Adenocarcinomas are malignant tumors in dogs that can occur in different organs. Occasional signs were weight loss vomiting and rarely diarrhea. In dogs adenocarcinoma is the most common gastric and large intestinal neoplasm whereas lymphoma is more frequently seen in the small intestine followed by adenocarcinoma and sarcomas such as gastrointestinal stromal tumor GIST and leiomyosarcoma.
There are two types of colon cancers that can affect dogs. Vet bills can sneak up on you. Colorectal adenocarcinoma was diagnosed in 78 dogs.
In conclusion ultrasonography is a useful tool in the diagnosis of papillary adenocarcinoma of the descending colon in dogs and surgical resection combined with adjuvant chemotherapy can provide superior disease-free survival time with good quality of life. Adenocarcinomas are often classified as infiltrative expansile sometimes with ulcer formation polypoid nodularcobblestone and annular based on the biopsy and gross appearance. However adenomatous polyps and carcinoma in situ are also regularly diagnosed.
This means that they spread to other organs. Adenocarcinoma of the descending colon in dogs and surgical resection combined with adjuvant chemotherapy can provide superior disease-free survival time with good quality of life. Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumor originating in the glandular and epithelial tissue the lining of the internal organs.
Early detection and aggressive treatment are essential in the successful management of this tumor. Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum can present as unintentional weight loss fatigue generalized weakness hematochezia abdominal pain bowel obstruction. Prognosis for dogs with non lymphomatous small intestinal tumors treated by surgical excision.
Sixty- eight cases of intestinal adenocarcinoma in the cat excluding duodenal ade- nocarcinoma have been reported 8. Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma. This type of malignant tumor growth can take place in many parts of the body including the gastrointestinal system of dogs.
Other reported canine GI neoplasms include carcinoid adenoma leiomyoma carcinoma in situ and.